Where p is momentum, m is mass and v is velocity. Momentum is a vector quantity and has the units Newton seconds. Momentum can also be defined with a slight alteration to Newton's 2nd Law.
Take:
The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma
alter to:
The rate of change of momentum is
directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and the direction of
the net force.
F = ma can be rewritten as:
which can be rewritten as:
Impulse is known as change in momentum. Impulse can also be written as below:
From this point, we will move onto conservation of momentum.
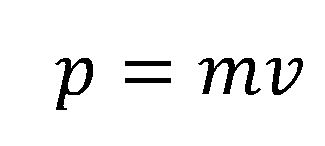



No comments:
Post a Comment